As residential solar energy becomes increasingly popular worldwide, more homeowners are exploring grid-tied photovoltaic (PV) systems to reduce electricity costs and achieve energy independence. However, many face technical, regulatory, and efficiency challenges. This article explains what a grid-tied solar system is, common issues homeowners encounter, and how smart metering solutions like Acrel’s ADL series can help.
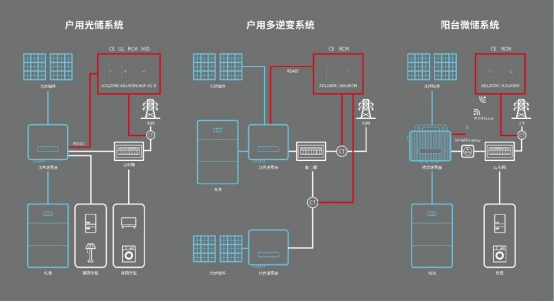
A grid-tied solar system refers to a residential photovoltaic setup connected to the local utility grid. It typically consists of solar panels, an inverter, and optional energy storage. Unlike off-grid systems, a grid-tied setup allows bidirectional energy flow:
- Excess solar power can be fed back into the grid, often earning credits or payments through net metering programs.
- When solar generation is insufficient—such as at night or on cloudy days—the home draws power from the grid.
This setup is ideal for homeowners looking to lower electricity bills while maintaining a reliable power supply.
Typical users include:
- 1. Families in regions with high electricity prices and abundant sunlight
- 2. Small farms with irrigation or greenhouse loads
- 3. Property developers integrating solar into new housing projects

Despite the benefits, many users encounter practical and regulatory hurdles:
▲ Low Generation Efficiency & Unclear Returns
Factors like shading, dirt, or inverter faults can reduce system output. Without accurate monitoring, homeowners cannot pinpoint underperforming components or verify feed-in tariff earnings.
▲ Grid Compliance & Anti-Islanding Requirements
In many countries—especially across Europe, North America, and parts of Asia—grid-tied systems must prevent reverse power flow to avoid overloading local transformers, causing voltage instability, or endangering utility workers during outages. Non-compliance can result in heavy fines.
▲ High Maintenance Costs & Difficult Fault Detection
Residential solar systems are often geographically dispersed, making manual inspections costly and slow. Early detection of voltage anomalies, meter errors, or communication failures is challenging without remote monitoring.
To address these challenges, Acrel’s ADL series energy meters offer tailored solutions for residential solar monitoring and control:
Key Features:
· Class 1 accuracy for reliable billing and subsidy calculations
· Bidirectional metering to track solar generation, grid import/export, and self-consumption
· Anti-reverse power monitoring with fast response to support inverter curtailment
· Wi-Fi/Bluetooth & RS485/Modbus connectivity for easy integration with home apps or professional EMS platforms
· Compact DIN-rail design, IP20 rating, and wide operating temperature range (-20°C to 60°C)
Model Selection Guide
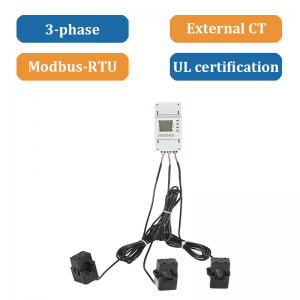
1. ADL200 series – For single-phase systems
ADL400 series – For three-phase systems
2. N models – Basic metering
M models – Dual-circuit measurement (PV + load/storage)
W models – Wireless communication for easy setup and remote access.
Global Compliance & Integration
ADL meters support essential regional certifications (CE, UL, SAA, etc.) and are already deployed with partners like Skyworth, WattEdge, and Hoymiles in various international markets.
Post time: Dec-15-2025